ARMY TM 9-6115-644-24
AIR FORCE TO 35C2-3-446-12
MARINE CORPS TM 09249A/09246A-24/2
GENERATOR
STATOR
EXCITER
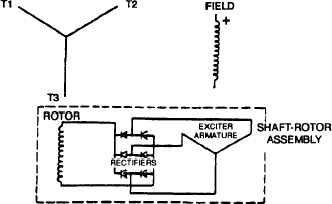
FIGURE 4-10. Brushless Generator Schematic
To energize the field, DC excitation must be applied to the generator field coils. The excitation current is supplied from a
brushless exciter mounted on the generator shaft.
The brushless exciter is actually an AC generator with its output rectified through a full wave bridge circuit. This type of
brushless exciter will provide the necessary excitation current. The generator set field flash circuit, activated during each
engine start, applies voltage to the exciter stator to begin the voltage build-up process to energize the generator field.
The generator output voltage is controlled by controlling the alternating field current. This is accomplished by
regulating the exciter field coil voltage. The exciter field coil voltage is regulated with a solid-state-type voltage regulator.
4-16-2 Damper Bars are inserted through the field laminations and welded at the end to a solid copper plate.
The damper windings provide stable parallel operation, reduce damping current losses, and limit the increase of third har-
monic voltage with increase in load.
4-16-3 Brushless Exciter The brushless exciter consists of an armature with a three-phase AC winding and rotating rectifi-
er assembly within a stationary field.
The stationary exciter field assembly is mounted in the main generator frame. The exciter armature is press fit and
keyed onto the shaft assembly. The rotating rectifier assembly slides over the bearing end of the generator rotor shaft and
is secured with bolts and washers to an adapter hub which is shrunk on the generator shaft.
4-16-4 Rotating Rectifier Bridge. The rotating rectifier bridge consists of rectifying diodes mounted on a brass heat sink
which is in turn mounted on an insulating ring. The entire assembly bolts to the adapter on the generator shaft. Therefore,
the rotating rectifier assembly will rotate with the exciter armature eliminating the need for any sliding contacts between
the exciter output and the alternator field.
4-16-5 Exciter Field.
The exciter field on the high frequency exciter consists of laminated segments of high carbon steel
which are fitted together to make up the field poles. The field coils are placed into the slots of the field poles.
4-16-6 Exciter Field Coil Voltage Source. Field coil DC voltage is obtained by rectifying the voltage from a phase to neutral
line of the generator output, or other appropriate terminal to provide the needed voltage reference.
The rectifier bridge is an integral part of the static regulator. The static regulator senses a change in the generator
output and automatically regulates current flow in the exciter field coil circuit to increase or decrease the exciter field
strength. An external adjust rheostat sized to be compatible with the regulator is used to provide adjustment to the regulator
sensing circuit.
4-31