TM 9-6115-729-24
0003
ENGINE COOLING SYSTEM - Continued
All of the coolant passes through the core of the oil cooler and the coolant enters the cylinder block internal
water manifold. The manifold disperses the coolant to water jackets around the cylinder walls. From the cylinder
block, the coolant flows into passages in the cylinder head. The passages send the flow around the unit injector
sleeves and the inlet and the exhaust passages. The coolant now enters the thermostat housing at the front
right side of the cylinder head. The thermostat controls the direction of flow. When the coolant temperature
is below the normal operating temperature, the thermostat is closed. The coolant is directed through a bypass
hose and into the top inlet of the water pump. When the coolant temperature reaches the normal operating
temperature, the thermostat opens. When the thermostat is open, the bypass is closed. Most of the coolant goes
through the outlet to the radiator for cooling. The remainder flows through bypass hose and into the water pump.
The shunt line extends from the top of the water pump to the surge tank. The shunt line must be routed properly
to avoid trapping any air. By providing a constant flow of coolant to the water pump, the shunt line prevents
cavitation. The lower GSC display indicates the engine coolant temperature.
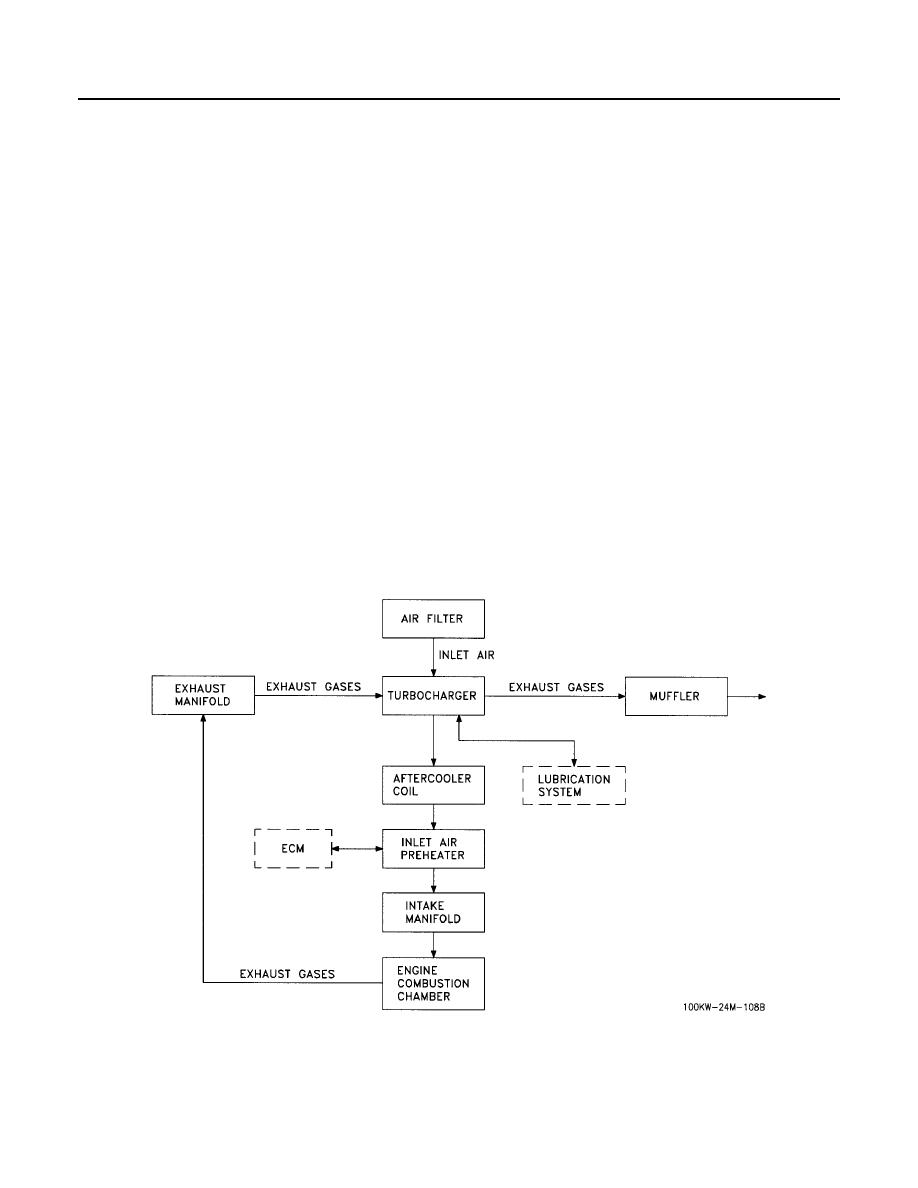
AIR INLET AND EXHAUST SYSTEM
The air inlet and exhaust system (Figure 6) consists of an air filter assembly, intake manifold,
turbocharger, exhaust manifold and muffler. Ambient air is drawn into the air filter assembly where it passes
through the filter elements. Airborne dirt is removed and trapped in the elements. Filtered air is drawn out of the
air filter assembly through air intake tubes to the turbocharger where it is pressurized and passed through an
aftercooler coil in the radiator. In cold weather, an inlet air preheater is activated to warm the inlet air. The
pressurized inlet air enters the intake manifold to the combustion chambers and mixes with fuel from the fuel
injectors. The engine exhaust gases are released into the turbocharger, which is mounted on the exhaust
manifold. The exhaust gases drive the turbocharger, forcing large amounts of air into the intake manifold. After
passing through the turbocharger, the exhaust gases are channeled into a muffler to deaden the sound. The
exhaust gases are vented upward from the generator set housing.


